Indian Man Builds Electric Car At Home; Shares Full DIY Video


The electric car segment is booming in India. Low operational costs is one of the reasons which lure people into buying an electric vehicle (EV). Another reason is the fascination towards driving something that is silent and smooth. Over the years, we have seen many build their own custom electric vehicles at home. Most of these aren't just college projects. Many excel with their build quality and efficiency. We have seen many build their own EVs, but getting to see someone film the entire process and share of YouTube is unusual. Now one such video has surfaced.
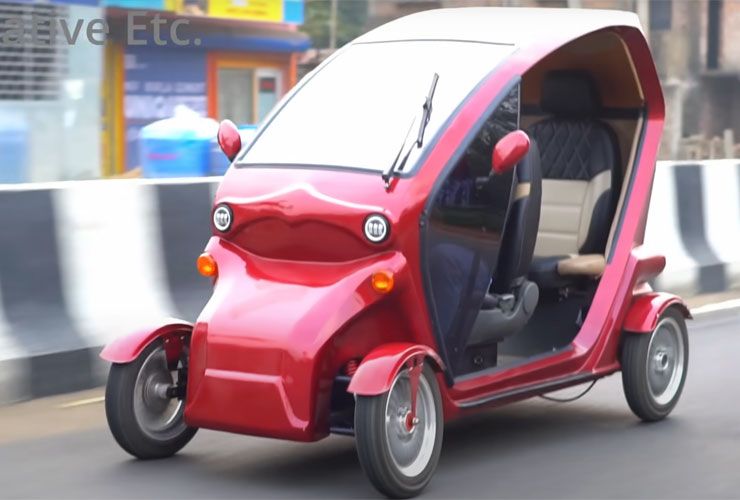
This video has been shared on the 'Creative Etc' channel. It shows a man building an EV (which he prefers to call a 'Mini Electric car') from scratch. The vehicle could look like a fancy e-rikshaw or an electric trike to many. It, however, has four wheels, instead of three. The design is simple and good-looking. It has been custom fabricated. You can see Carbon fibre vinyl in various areas of design. Two people can be accommodated in this vehicle.
The man starts by making the sketch first. It shows the overall structure and tentative measurements. The chassis is made from 2-inch rectangular bar. These are cut and joined together carefully. The skeleton for the top hat is made by using 1-inch Iron pipe.
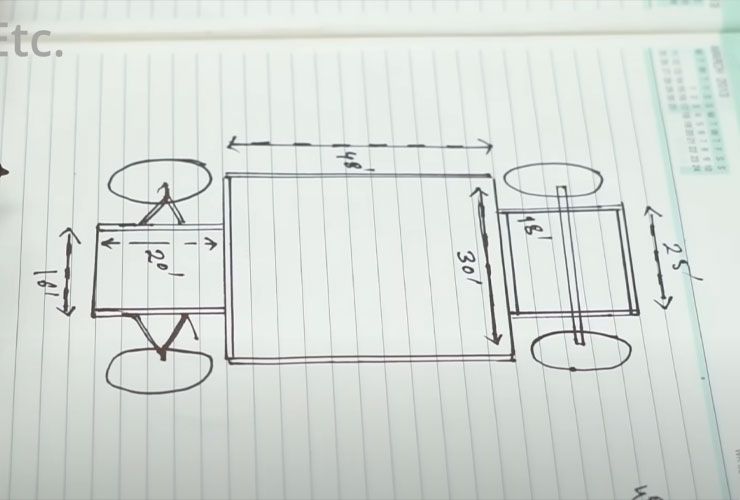
Talking of the dimensions, this vehicle spans 90 inches in length (the structure), and 30 inches in width. It has a ground clearance of 7 inches and a height of 58 inches.
The suspension of this 'mini electric car' four shocks sourced from the Hero Glamour motorcycle, one on each wheel. It rides on 12-inch electric rikshaw wheels with low-resistance tyres. The differential too is sourced from e-rikshaw.
The powerhouse here is a 1000W Brushless Direct Current (BLDC) electric motor that powers the rear axle. The electric motor and controller have both been sourced from 'E-MAXX'. The controller (aka micro-controller or Motor Control Unit (MCU)), manages the flow of electric power between the battery and motor. It is actively involved in deciding acceleration and direction of it.

The MCU, in a way, acts as an interface between the battery, the motor, and the driver's input (throttle, brakes, etc.). It converts the DC current from the battery pack to AC current for AC electric motors. In vehicles such as this, which use DC motors, the MCU regulates the DC power flow to the motor. It thus regulates speed and torque. It is the controller that reverses the motor rotation to pull off regenerative braking. Not sure if thie particular vehicle is equipped with regen.

The battery pack here is a 60V Lithium-ion unit. We don't have data on the acceleration, range, charging time and top speed of the vehicle yet.
The steering mechanism comes from an old car and so do the seats. The seats have, however, been reinforced with additional cushioning and good-looking upholstery. The roof gets a new roof liner.
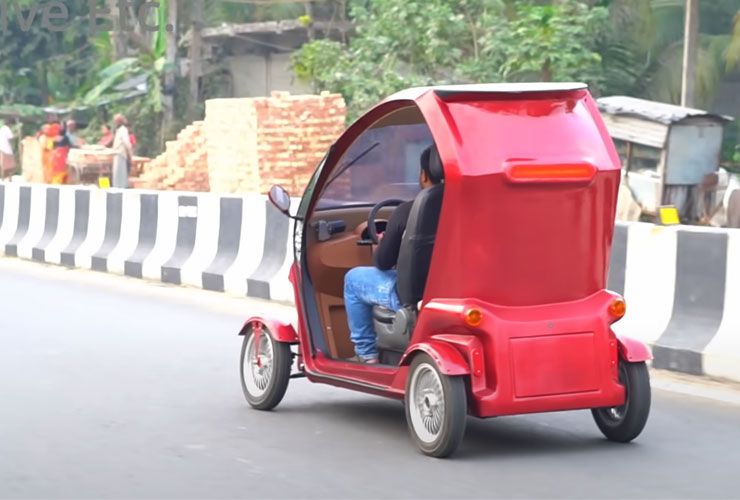

This vehicle has also been fitted with a 5-inch reverse parking camera and a universal sports steering wheel. The instrument cluster is a fully digital unit. In addition to the essential driver information, it also shows a speedometer and battery levels. For smooth operations in rain, the vehicle also has a large single wiper.